Hymenolepis microstoma (Rodent tapeworm) Assembly and Gene Annotation
NOTE: The genome sequence and annotation for this nematode are updated in Ensembl Metazoa infrequently. For the latest genome and annotation, please visit WormBase ParaSite.
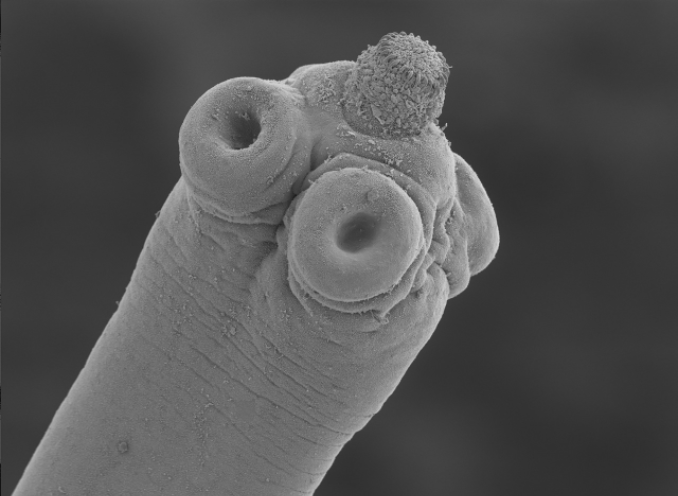
About Hymenolepis microstoma
Hymenolepis microstoma is a member of the Cyclophyllidea, which comprises the majority of tapeworms that are of medical importance. The cestode Hymenolepis microstoma, or rodent tapeworm, is an intestinal dwelling parasite of mice and rats which is used as a laboratory model organism. Adult worms live in the bile duct and small intestines, using beetles as intermediate hosts. H. microstoma is prevalent in rodents worldwide causing hymenolepiasis, but rarely infects humans. In humans, hymenolepiasis is caused by two other tapeworms, Hymenolepis nana (the dwarf tapeworm) and Hymenolepis diminuta (rat tapeworm). Heavy infections can cause weakness, headaches, anorexia, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
As a parasite that is using natural hosts that are themselves model organisms, H. microstoma has been used as a tapeworm research model. A lot of our understanding of the basic biology of tapeworms and hymenolepiasis in humans and other animals stems from work on this species.
Picture credit: Magdalena ZZ Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons (Image source)
Assembly
The H. microstoma genome was sequenced by the Berriman lab at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, in collaboration with Pete Olson (Natural History Museum, London). The initial version of the genome was described in Tsai et al (2013). Assembly presented here is the third consecutive version of the assembly HMN_v3, created by scaffolding a de novo PacBio assembly using Bionano's hybrid scaffolder (optical mapping). Further improvement was then carried out in gap5 using all the available optical map and sequence data.
Annotation
The annotation was produced by running BRAKER, incorporating de novo gene predictions and RNASeq alignments, predicted on an unmasked assembly. The resulting predictions were then clustered using OrthoMCL and repeated predictions in low-complexity and repeat regions manually removed. A number of gene models were manually curated using Apollo.
- Complete representation of a tapeworm genome reveals chromosomes capped by centromeres, necessitating a dual role in segregation and protection.
Olson PD, Tracey A, Baillie A, James K, Doyle SR, Buddenborg SK, Rodgers FH, Holroyd N, Berriman M. 2020. BMC Biol, 2020;18(1):165. - Genome-wide transcriptome profiling and spatial expression analyses identify signals and switches of development in tapeworms.
Olson PD, Zarowiecki M, James K, Baillie A, Bartl G, Burchell P, Chellappoo A, Jarero F, Tan LY, Holroyd N, Berriman M. 2018. Evodevo, 2018;9():21 - Description of Hymenolepis microstoma (Nottingham strain): a classical tapeworm model for research in the genomic era.
Cunningham LJ, Olson PD. 2010. Parasit Vectors, 2010;3():123
- The genomes of four tapeworm species reveal adaptations to parasitism.
Tsai IJ, Zarowiecki M, Holroyd N, Garciarrubio A, Sánchez-Flores A, Brooks KL, Tracey A, Bobes RJ, Fragoso G, Sciutto E, Aslett M, Beasley H, Bennett HM, Cai X, Camicia F, Clark R, Cucher M, De Silva N, Day TA, Deplazes P, Estrada K, Fernández C, Holland PWH, Hou J, Hu S, Huckvale T, Hung SS, Kamenetzky L, Keane JA, Kiss F, Koziol U, Lambert O, Liu K, Luo X, Luo Y, Macchiaroli N, Nichol S, Paps J, Parkinson J, Pouchkina-Stantcheva N, Riddiford N, Rosenzvit M, Salinas G, Wasmuth JD, Zamanian M, Zheng Y, Taenia solium Genome Consortium, Cai J, Soberón X, Olson PD, Laclette JP, Brehm K, Berriman M. 2013. Nature, 2013;496(7443):57-63.
Picture credit: File:Hymenolepis microstoma.jpg provided by Dr. Magdalena Zarowiecki. This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
Links
Statistics
Summary
| Assembly | HMN_v3, INSDC Assembly GCA_000469805.3, |
| Database version | 115.1 |
| Golden Path Length | 168,943,216 |
| Genebuild by | Wellcome Sanger Institute |
| Genebuild method | Import |
| Data source | Wellcome Sanger Institute |
Gene counts
| Coding genes | 10,139 |
| Gene transcripts | 11,429 |



![Follow us on Twitter! [twitter logo]](/i/twitter.png)
