Search
NOTE: The genome sequence and annotation for A. suum are updated in Ensembl Metazoa infrequently. For the latest genome and annotation, please visit WormBase ParaSite.
About Ascaris suum
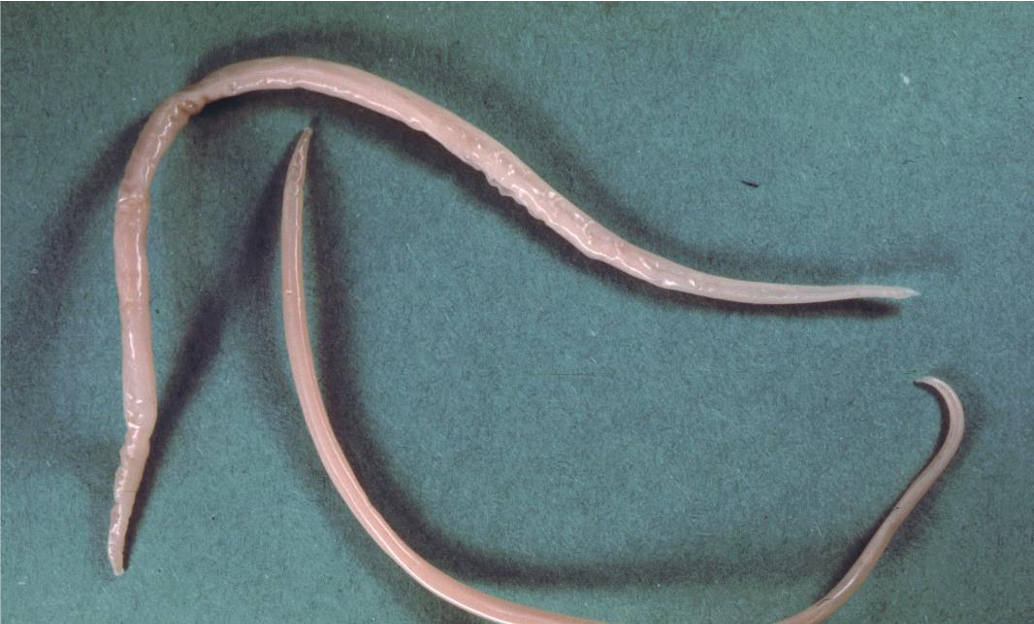
Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematodes that can cause infections in humans and pigs. The roundworm Ascaris suum, is an intestinal parasite of pigs causing ascariasis and it has been characterised as the most damaging worm of swine. It is also known as the “large roundworm of pig”. Ascariasis is a soil-transmitted infection caused by ingesting the eggs of Ascaris suum. After a maturation process which takes place in the intestines, liver and lungs, the larvae will get swallowed again and will end up in the small intestine where the adult worms will emerge. Ascariasis in pigs is causing an increased feed to gain ratio and liver condemnation, while the migration of larvae through the lungs has been associated with secondary bacterial infections and cute respiratory symptoms in pigs. The eggs produced by the adult worms, which end up in the feces, and are extremely resistant to environmental conditions and disinfectants, remaining infective in the environment for years.
A. suum is closely related to A. lumbricoides, the human large roundworm parasite, one of the most common human parasitic infections in the world. Cross infections of A. suum to humans and A. lumbricoides to pigs have been reported.
Picture credit: Alan R Walker Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons (Image source)
Taxonomy ID 6253
Data source University of Colorado Denver
Comparative genomics
What can I find? Homologues, gene trees, and whole genome alignments across multiple species.
 More about comparative analyses
More about comparative analyses
 Phylogenetic overview of gene families
Phylogenetic overview of gene families
 Download alignments (EMF)
Download alignments (EMF)
Variation
This species currently has no variation database. However you can process your own variants using the Variant Effect Predictor:



 Display your data in Ensembl Metazoa
Display your data in Ensembl Metazoa
 Update your old Ensembl IDs
Update your old Ensembl IDs

![Follow us on Twitter! [twitter logo]](/i/twitter.png)
