Schmidtea nova (Flatworm, GOE00023_SP068/2) Assembly and Gene Annotation
About Schmidtea nova
The genus Schmidtea comprises four species of freshwater planarians, predominantly found in Europe, with some populations also present in north Africa, Asia and introduced in regions of America [2,4]. Schmidtea nova is a poorly studied species and has only been morphologically desctibed very recently [4]. Schmidtea nova is reported only from a few localities ranging from northern Italy in the south to Sweden in the north, and eastward to Romania (see [4] for a summary). This broad yet sparse distribution suggests that S. nova may be more widespread and abundant than suggested by the current species records.
Little is known about the life cycle of Schmidtea nova. Observed populations reproduce through the deposition of egg capsules. Its karyotype consists of a diploid chromosome number of 2n = 6, differing from the 2n = 8 characteristic of other Schmidtea species, including its sister species Schmidtea lugubris. Interestingly, S. nova appears to induce a developmental response in embryos of the frog species Rana temporaria, which it preys upon [5].
The S. nova strain (internal ID: GOE00023) was collected at 51,0717710 and 13,7421400 in Dresden, Germany, on 2013-04-14.
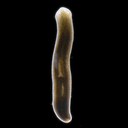
Picture credit (Creative Commons BY 4.0): Miquel Vila-Farré, Dept. of Tissue Dynamics and Regeneration, Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences
Taxonomy ID 163373
Assembly
The assembly presented here has been imported from INSDC and is linked to the assembly accession [GCA_044892505.1].
PacBio Circular consensus sequencing reads were called using pbccs (v6.0.0) and reads with quality > 0.99 (Q20) were taken forward as “HiFi” reads. To create the initial contig assemblies from 30x PacBio HiFi reads (SRA: SRR27325391), canu v2.1 was used with parameters: maxInputCoverage=100 -pacbio-hifi. Next, alternative haplotigs were then removed using purge-dups (v1.2.3) using default parameters and cutoff as they were correctly estimated by the program. To initially scaffold the contigs into scaffolds, SALSA v2 (v2.2) was used after mapping Hi-C reads (SRA: SRR27325343) to the contigs. The VGP Arima mapping pipeline was followed: https://github.com/VGP/vgp-assembly/tree/master/ pipeline/salsa using bwa-mem (v0.7.17), samtools (v0.10, v1.11) and Picard (v2.22.6). False joins in the scaffolds were then broken and missed joins merged manually following the processing of Hi-C reads with pairtools (v0.3.0) and visualization matrices created with cooler (v0.8.11). Following scaffolding, the original PacBio subreads were mapped to the chromosomes using pbmm2 (v1.3.0, https://github.com/ PacificBiosciences/pbmm2) with arguments: --preset SUBREAD -N 1 and regions +/− 2 kb around each gap were polished using gcpp’s arrow algorithm (v1.9.0). Those regions in which gaps were closed and polished with all capital nucleotides (gcpp’s internal high confidence threshold) were then inserted into the assemblies as closed gaps. Lastly, the PacBio HiFi (CCS reads with a read quality exceeding 0.99) were aligned to the genomes using pbmm2 (v1.3.0) with the arguments --preset CCS -N 1. DeepVariant (v1.2.0,98) was used to detect variants in the alignments to the assembled sequence. Only the homozygous variants (GT = 1/1) that passed DeepVariant’s internal filter (FILTER = PASS) were retained using bcftools view (v1.12) and htslib (v1.11). The genome was then polished by creating a consensus sequence based on this filtered VCF file, as detailed in the VGP assembly pipeline (https://github.com/VGP/vgp-assembly/tree/ master/pipeline/freebayes-polish).
The assembly was produced by "Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences" and reported in [3].
The total length of the assembly is 1251382582 bp contained within 283 scaffolds. The scaffold N50 value is 455729997, the scaffold L50 value is 2. The GC% content of the assembly is 28.0%.
Annotation
Genomic annotation was provided by "Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences".
The genome was annotated using a hybrid genome-guided transcriptome approach. As input RNAseq data, we combined Nanopore direct RNA-seq of pooled whole animals at various feeding stages and regeneration stages (SRA: SRR27325397), Nanopore cDNA RNA-seq of whole animals (SRA: SRR27325399) and a regeneration series (SRA: SRR27325398). Total RNA was extracted from snap-frozen planarian tissue using the protocol described in [1,3].
After read quality trimming, deduplication, filtering, and mapping (using HISAT2 and minimap2 for short and long reads, respectively), a draft transcriptome was generated using Stringtie2 then it was further refined using FLAIR and a collection of custom scripts to filter high- confidence isoforms. For details of the procedure and a step-by-step guide to the genome annotation analysis, see the Supporting Information of [3].
Small RNA features, protein features, BLAST hits and cross-references have been computed by metazoa.
References
Grohme M. A., S. Schloissnig, A. Rozanski, M. Pippel, G. R. Young, S. Winkler, H. Brandl, I. Henry, A. Dahl, S. Powell, M. Hiller, E. Myers, and J. C. Rink. 2018. The genome of Schmidtea mediterranea and the evolution of core cellular mechanisms. Nature 554:56–61.
Ball IR. 1969. Dugesia lugubris (Tricladida: Paludicola) a European immigrant into North American fresh waters. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada 26, 221–228.
Ivanković M., J. N. Brand, L. Pandolfini, T. Brown, M. Pippel, A. Rozanski, T. Schubert, M. A. Grohme, S. Winkler, L. Robledillo, M. Zhang, A. Codino, S. Gustincich, M. Vila-Farré, S. Zhang, A. Papantonis, A. Marques, and J. C. Rink.
A comparative analysis of planarian genomes reveals regulatory conservation in the face of rapid structural divergence. Nat Commun 15:8215.
Leria, L., et al. 2018. Diversification and biogeographic history of the Western Palearctic freshwater flatworm genus Schmidtea (Tricladida: Dugesiidae), with a redescription of Schmidtea nova. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research 56(3): 335-351.
Segev, O., Rodríguez, A., Hauswaldt, S., Hugemann, K., and Vences, M. 2015. Flatworms (Schmidtea nova) prey upon embryos of the common frog (Rana temporaria) and induce minor developmental acceleration. Amphibia-Reptilia 36: 155-163.
Statistics
Summary
| Assembly | ASM4489250v1, INSDC Assembly GCA_044892505.1, |
| Database version | 115.1 |
| Golden Path Length | 1,251,382,582 |
| Genebuild by | Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences |
| Genebuild method | Import |
| Data source | Max Planck Institute for Multidisciplinary Sciences |
Gene counts
| Coding genes | 18,709 |
| Non coding genes | 22,830 |
| Small non coding genes | 22,830 |
| Gene transcripts | 57,075 |



![Follow us on Twitter! [twitter logo]](/i/twitter.png)
